Antrodia cinnamomea found to protect against hepatic injury and inflammation
06/07/2019 / By Evangelyn Rodriguez
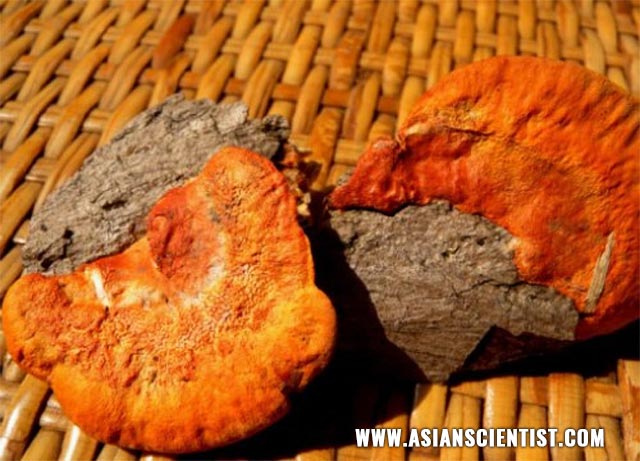

In this study, researchers from National Taiwan Normal University investigated the anti-inflammatory effect of Antrodia cinnamomea, a medicinal mushroom in Taiwan, and the molecular mechanisms underlying its activity. The results of their study were published in The American Journal of Chinese Medicine.
- A. cinnamomea is widely used in Taiwan to prevent or treat liver disease.
- The researchers used water as extraction solvent to obtain water extracts from A. cinnamomea (ACW).
- They used HPLC fingerprint analysis and identified seven ergostane-type triterpenoids from ACW, including high amounts of antcin K (AC), antcin C, antcin H, dehydrosulphurenic acid, antcin B, antcin A, and dehydroeburicoic acid.
- They examined the effects of ACW and AC – which had the highest amount in ACW – on N-nitrosodiethylamine (DEN)-induced liver inflammation, fibrosis, and carcinogenesis in rats.
- For the in vitro study, the researchers measured how ACW and AC dose-dependently scavenged O?.2, H2O2 and HOCl using a chemiluminescence analyzer.
- For the in vivo experiment, they found that oral intake of ACW and AC significantly inhibited DEN-enhanced hepatocellular inflammation, fibrosis, and carcinoma.
- ACW and AC also reduced the amounts of elevated bile and liver reactive oxygen species (ROS).
- In addition, ACW and AC inhibited plasma y-glutamyl transpeptidase and oxidative stress, including 3-nitrotyrosine, 4-hydroxynonenal, and Kuppfer cell infiltration (ED-1 stains) in the inflammatory livers.
- While DEN enhanced nuclear factor-kB (NF-kB) translocation, ACW and AC suppressed DEN-enhanced NF-kB translocation by inhibiting its upstream signaling of p85/phosphoinositide-3-kinase, mitogen-activated protein kinase, and CYP2E1 expression.
The researchers concluded that A. cinnamomea and its active component, antcin K, counteract DEN-induced hepatic injury and inflammation by scavenging ROS activity and upregulating antioxidant defense mechanisms.
Journal Reference:
Tien AJ, Chien CY, Chen YH, Lin LC, Chien CT. FRUITING BODIES OF ANTRODIA CINNAMOMEA AND ITS ACTIVE TRITERPENOID, ANTCIN K, AMELIORATES N-NITROSODIETHYLAMINE-INDUCED HEPATIC INFLAMMATION, FIBROSIS AND CARCINOGENESIS IN RATS. The American Journal of Chinese Medicine. 2017;45(01):173–198. DOI: 10.1142/s0192415x17500124
Tagged Under: alternative medicine, antcin C, anti-inflammatory, anticancer, antioxidants, Antrodia cinnamomea, cancer cures, cancer treatment, disease treatments, edible fungi, edible fungus, food cures, food is medicine, functional food, hepatocellular carcinoma, Hepatoprotective, herbal medicine, Herbs, inflammation, liver disease, liver fibrosis, medicinal mushroom, mushroom, natural cures, natural medicine, prevention, remedies, research, TCM, traditional Chinese medicine, triterpenoids
RECENT NEWS & ARTICLES
COPYRIGHT © 2017 RESEARCH NEWS