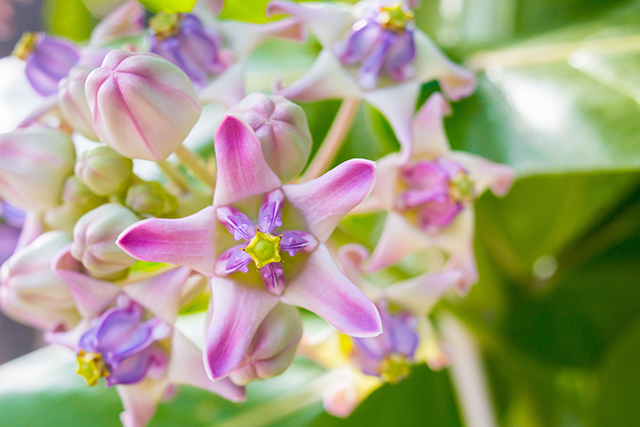
Calotropis gigantea promotes the formation of synapses and neurites in the hippocampus
07/25/2019 / By Evangelyn Rodriguez

Researchers from Dongguk University Graduate School of Medicine and Pukyong National University in South Korea investigated the neuromodulatory effects of ethanol extracts obtained from the leaves of Calotropis gigantea, a plant with a long history of use in traditional medicine. The results of their study were published in The American Journal of Chinese Medicine.
- C. gigantea, commonly known as milkweed or crown flower, is a large shrub that grows in temperate regions of Asia, including China, Bangladesh, and India.
- For their study, the researchers obtained extracts from C. gigantea leaves (CGE) and evaluated their effects during synaptogenesis in the late stages of neural development and during early stage neuritogenesis using rat hippocampal neurons.
- The researchers reported that CGE at a concentration of 7.5 ug/ml facilitated the early development of cytoarchitecture, as evidenced by increases in morphometric parameters, such as the numbers, lengths, and number of branches of initial neurites, axon, and dendrites.
- Through immunocytochemistry, they found that CGE upregulated synaptic vesicle 2 (SV2, a marker of axon terminals) and postsynaptic density-95 (PSD-95, a postsynaptic marker) and their colocalization during the synaptogenic stage (DIV 14).
- CGE also upregulated nerve growth factor (NGF) and activated extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 (Erk1/2), which is blocked by a TrkA-specific inhibitor. This activity suggested that the neuritogenic and synaptogenic potential of CGE is due to its ability to activate NGF-TrkA-Erk1/2 signaling.
- When researchers analyzed CGE using ultra performance liquid chromatography, they did not detect stigmasterol, an active component of C. gigantea. Despite this, chloroform-methanol and ethyl acetate subfractions of CGE exhibited initial neuritogenic activity, suggesting that the neurotrophic-mimetic properties of CGE are due to multiple active components.
Based on these results, the researchers concluded that CGE has neuromodulatory activity and contains as yet unidentified active phytochemicals with potential nootropic, protective, or therapeutic effects on the human brain.
Journal Reference:
Haque MN, Mohibbullah M, Hong YK, Moon IS. CALOTROPIS GIGANTEA PROMOTES NEURITOGENESIS AND SYNAPTOGENESIS THROUGH ACTIVATION OF NGF-TRKA-ERK1/2 SIGNALING IN RAT HIPPOCAMPAL NEURONS. The American Journal of Chinese Medicine. 2018;46(08):1861–1877. DOI: 10.1142/s0192415x18500933
Tagged Under: alternative medicine, brain function, brain health, Calotropis gigantea, cognitive function, cognitive health, crown flower, herbal medicine, Herbs, hippocampus, medicinal plants, milkweed, natural cures, natural medicine, nervous system, neural development, neuritogenic, neuromodulatory, neurons, phytochemicals, plant components, research, stigmasterol, synapse formation, synaptogenic, TCM, traditional Chinese medicine
RECENT NEWS & ARTICLES
COPYRIGHT © 2017 RESEARCH NEWS