False starwort: Explore the many health benefits of the “ginseng of the lungs”
05/05/2020 / By Evangelyn Rodriguez

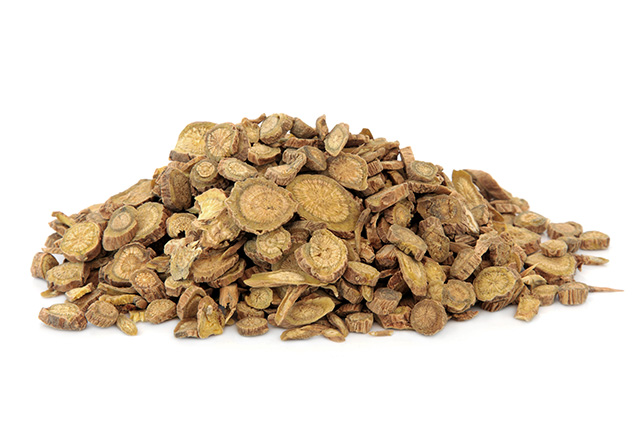
Pseudostellaria heterophylla, also referred to as false starwort or “ginseng of the lungs,” is a well-known traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) that has been used in China for centuries. In TCM, false starwort is used to invigorate the spleen, replenish qi, moisten the lungs and improve blood circulation.
Some of the common ailments addressed by this herb include anorexia, asthenia (abnormal physical weakness) after a severe illness, cough due to lung dryness, fatigue and spleen asthenia. Because of its mild effects, false starwort is often prescribed to children as a substitute for ginseng.
In a recent study, researchers at the University of Macau reviewed the chemical and pharmacological properties of P. heterophylla in order to understand its active components. They discussed their findings in an article published in the journal Chinese Medicine.
The biological properties and chemical components of false starwort
Due to its popularity in China, false starwort is cultivated on a large scale despite certain limitations in order to meet market demands. However, studies have found significant differences between wild and cultivated false starwort in terms of quality.
The researchers decided to review false starwort’s chemical properties and composition because they believe it is necessary to understand the herb’s chemical components and pharmacological activities before establishing an effective quality control method that ensures the safety and efficacy of cultivated products.
The researchers reported that, based on chemical analyses, false starwort is rich in cyclic peptides, polysaccharides, amino acids, saponins and sapogenins. While cyclic peptides like pseudostellarin, which has special structures, have attracted scientific interest recently, they are still being studied for their beneficial properties.
Polysaccharides, on the other hand, are some of the main bioactive components of false starwort. Besides having the ability to stop red blood cells from clumping together, these polysaccharides have also been found to inhibit the activities of enzymes involved in HIV infection. (Related: Scientists are looking at this African plant as a possible natural treatment for HIV.)
Other notable properties of false starwort that have been reported by studies include anti-diabetic, anti-tussive and antioxidant properties. Research also suggests that the herb has protective effects against retinal injury and exercise-induced oxidative stress.
The researchers noted that while false starwort is rich in oligosaccharides, these plant nutrients are rarely focused on by studies. In addition, although the herb’s properties have been analyzed numerous times, only a few of the analytical methods used in chemical studies are accepted as quality control methods.
The researchers are convinced that further investigations on the oligosaccharides present at high concentrations in false starwort aqueous extracts can lead to the development of rational and scientific quality control methods for this Chinese herb.
Medicinal uses of false starwort
Known in TCM as hai er shen or tai zi shen, the dried, tuberous root of false startwort is used as an anti-asthma and anti-HIV medicine. However, its best-known use is as an adaptogen. TCM practitioners also use false starwort as a remedy for dyspnea (difficulty breathing) and emphysema (shortness of breath). Due to its effectiveness against lung diseases and in relieving symptoms that affect the said organ, false starwort has been branded as the “ginseng of the lungs.”
Here are the benefits of using false starwort, according to TCM:
- Improves physical health and promotes recovery, especially after a serious illness
- Strengthens the spleen and treats loose stools
- Enhances the appetite
- Helps control blood sugar levels
- Promotes sound sleep
- Improves symptoms of neuroasthenia
- Serves as a good natural remedy for cough, palpitation, edema, dry mouth and other diseases
False starwort is a powerful herb with a variety of medicinal applications. If you’re planning to use it as an alternative or complementary medicine, consult with a natural health practitioner first. Like all potent herbal medicines, false starwort contains plenty of compounds that could interact with your current medication. To avoid any unwanted side effects, seek professional advice before using.
Sources include:
Tagged Under: alternative medicine, Chinese medicine, false starwort, ginseng of the lungs, herbal medicine, Herbs, natural cures, natural medicine, phytonutrients, plant medicine, quality control, remedies, research, TCM
RECENT NEWS & ARTICLES
COPYRIGHT © 2017 RESEARCH NEWS