Manage your cholesterol levels naturally with this Chinese herbal pill
09/04/2018 / By Ralph Flores
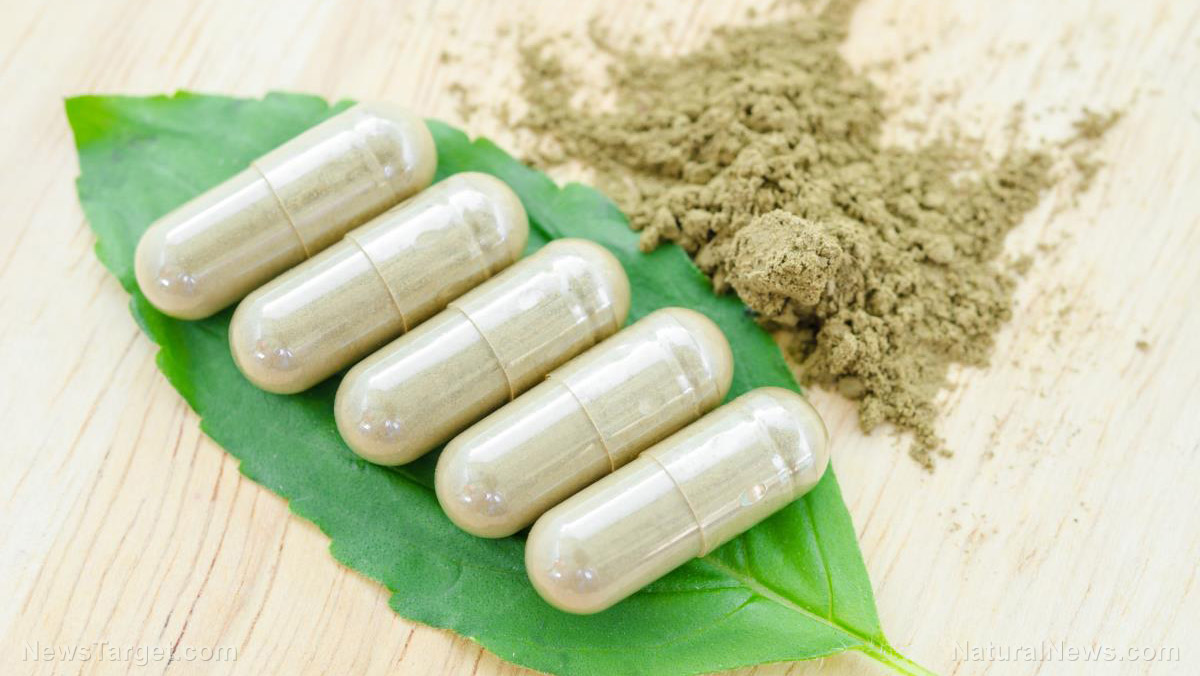

A study published in BMC Complementary and Alternative has identified two active ingredients in the Danqi pill – prescribed in Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) for heart disease – which can help improve metabolism and cholesterol levels. Researchers from the Beijing University of Chinese Medicine indicate that salvianolic acids, as well as saponins from Chinese ginseng (Panax notoginseng), regulate lipid metabolism in ischemic heart disease models.
Ischemic heart disease is a condition where the coronary arteries become narrowed because of a buildup of fatty material in the blood vessel. This impairs the supply of oxygen-rich blood to the cardiac muscles, ultimately leading to a heart attack. The condition is also referred to as coronary heart disease (CHD). According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, CHD is the most common cardiovascular disease. In the U.S., it claims 370,000 lives each year. (Related: Heart disease rates in U.S. vary by region, education level.)
There are medications available to manage the condition, but some of them come with adverse side effects. In the study, researchers pointed out that TCM has also been treating CHD, with the Danqi pill – an herbal medicine made from red sage (Salvia miltiorrhiza) and Chinese ginseng – being the most commonly prescribed one.
“This study will provide further insight into the mechanisms of traditional Chinese medicine in the management of CHD,” the researchers wrote in their report.
Researchers looked at how the main components of the Danqi pill, salvianolic acids and P. notoginseng saponins (DS), affect lipid metabolism disorders that are associated with cardiovascular diseases such as CHD. For the study, Sprague-Dawley rats were randomly assigned into five groups: sham-operated, model, positive control drug (clofibrate) treated, solutions of DS treated, and Danqi pill treated groups. Aside from the sham-operated group, the rats underwent left anterior descending (LAD) artery ligation surgeries to induce ischemic heart disease. They were then given a high-fat diet for 28 days. Those in the Danqi pill and the DS treated groups, however, were provided with their regular dosage daily.
The rats that were treated with both DS and Danqi pill had better cardiac functions than other groups. In particular, researchers identified that both treatments had cardioprotective activities in ischemic heart disease and can prevent enlargement of the heart muscles. This activity, they wrote, could be attributed to the ability of both DS and Danqi pill to improve cardiac energy metabolism and up-regulate transcription factors such as PPAR?, PPAR?, and PGC-1? – which are linked to protecting the heart under ischemic conditions. Both Danqi pill and DS treatments improved cardiac functions in an ischemic heart model. The two also up-regulated mRNA expression of lipoprotein lipase (LPL), an enzyme known to break down fat, as well as other expressions like FABP4 and CPT-1A. DS treatments, however, showed better results than the Danqi pill on PGC-1?, a regulator of energy metabolism and a coactivator of PPARs.
“DS are the major effective components of DQP [Danqi pill] in improving energy metabolism in ischemic heart disease model,” the researchers concluded.”The effects of DQP and DS are comparable, indicating that DS are the major effective components in regulating energy metabolism.” Further studies, they added, will enable researchers to gain more insight into the mechanisms between salvianolic acids and P. notoginseng saponins and how they can be used to treat cardiovascular diseases.
Find other TCM procedures to beat heart disease by following ChineseMedicine.news today.
Sources include:
Tagged Under: alternative medicine, cardiovascular disease, cardiovascular health, coronary heart disease, Danqi pill, heart disease, heart health, herbal medicine, Herbs, inflammation, Ischemic heart disease, natural cures, natural medicine, Panax notoginseng, remedies, research, salvianolic acid, saponins, TCM, traditional Chinese medicine