Using the Jerusalem Artichoke to produce green cement
11/20/2018 / By RJ Jhonson

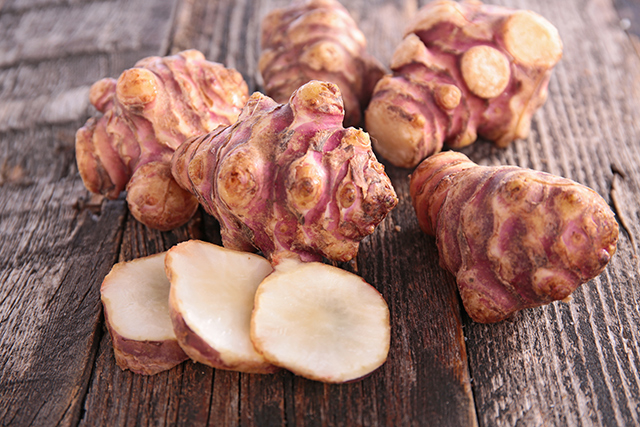
Concrete composites are being developed to address the weaknesses of conventional concrete. A study published in Industrial Crops and Products examined the merits of using Jerusalem artichoke (Helianthus tuberosus) stalk particles as a raw material for cement-bonded particleboards.
- The researchers produced and assessed cement-bonded particleboards measuring 300-by-300-10 millimeters and with a nominal density of 1250?kg/m3.
- They subjected the particleboards to two curing conditions:
- Forty-eight hours in a climatic chamber followed by 25 days in an air-saturated environment
- Forty-eight hours in a climatic chamber, followed by a dioxide carbon (15 percent concentration) environment for 24 hours, and followed by 24 days in an air-saturated environment.
- The boards were then put through both physical and mechanical characterization at 28 days.
- According to the researchers, the boards met the ISO 8335 Standard for concrete composites in building applications.
- Moreover, the particleboards demonstrated lower thickness swelling and water absorption than the values reported in previous literature and those in the Standards requirements.
Because of their findings, the researchers concluded that Jerusalem stalk particles are suitable for use as raw materials in concrete composites.
Find creative uses for vegetables at Veggie.news.
Journal Reference:
Cabral M, Nakanishi E, Mármol G, Palacios J, Godbout S, Lagacé R, Savastano H, Fiorelli J. POTENTIAL OF JERUSALEM ARTICHOKE (HELIANTHUS TUBEROSUS L.) STALKS TO PRODUCE CEMENT-BONDED PARTICLEBOARDS. Industrial Crops and Products. 6 June 2018;122:214-222. DOI: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2018.05.054
Tagged Under: cement, cement composite, concrete, conrete composite, Helianthus tuberosus, ISO 8335, Jerusalem Artichoke, natural fibers