Scientists: The Indian olive contains a variety of powerful antioxidants
08/02/2018 / By Michelle Simmons
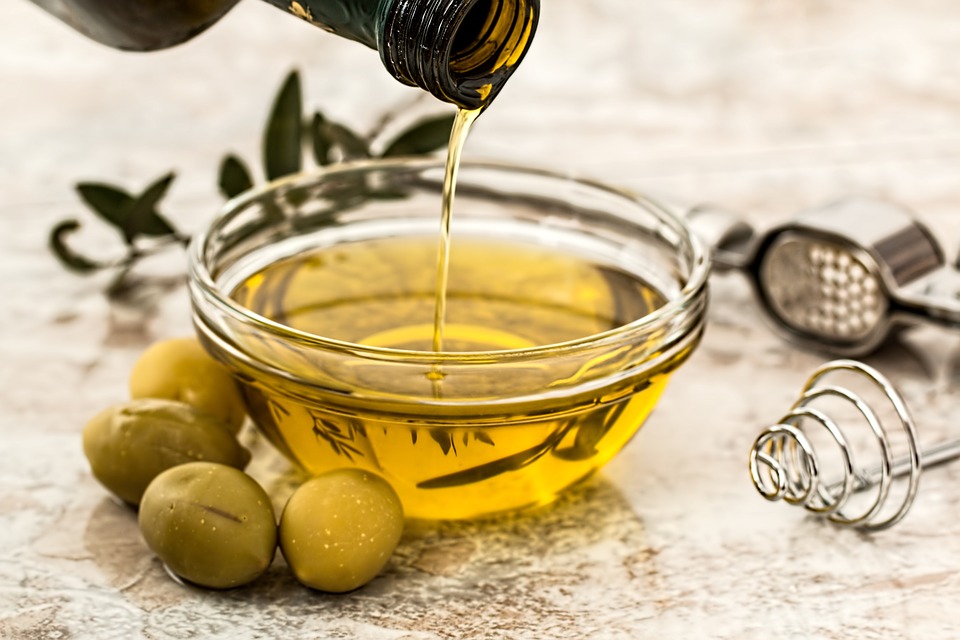

A study published in the journal BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine has found that the olive (Olea ferruginea Royle) contains a variety of powerful antioxidants that can treat infectious diseases. In the study, researchers at University of Azad Jammu and Kashmir in Pakistan looked at the phenolic contents, antimicrobial, and antioxidant activities of the olive plant.
- The olive plant has been known for treating infectious diseases.
- In the study, researchers used the leaf and bark chloroform, ethanol, and methanol extracts of olive.
- They identified the phenolic contents of olive leaf and bark extracts by Folin-Ciocalteu Spectrophotometric method.
- They evaluated the plant’s antimicrobial activity against gram-positive bacteria Bacillus subtilis and Staphylococcus aureus, gram-negative Escherichia coli, and yeast strains Candida albicans and Saccharomyces cerevisiae by disc diffusion method.
- Lastly, antioxidant activity was analyzed through the DPPH (2,2-diphenyl-1-picryl-hydrazyl-hydrate) assay.
- The bark extract of olive had the highest phenolic content.
- Both the ethanol and methanol extracts exhibited inhibitory activity against both gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria.
- Only the methanol extract of leaves demonstrated inhibitory activity against yeast strains.
- Chloroform extracts were found inactive against the bacteria and yeast strains tested.
- Methanol extracts of leaves and bark of olive had the highest antioxidant activities among the three crude extracts.
The study supports the use of the olive plant in traditional medicines for treating infectious diseases.
Read the full text of the study at this link.
To read more stories on medicinal plants, visit AlternativeMedicine.news today.
Journal Reference:
Mehmood A, Murtaza G. PHENOLIC CONTENTS, ANTIMICROBIAL AND ANTIOXIDANT ACTIVITY OF OLEA FERRUGINEA ROYLE (OLEACEAE). BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine. 5 June 2018; 18(173). DOI: 10.1186/s12906-018-2239-0
Tagged Under: Antimicrobial, antioxidant, food as cures, natural medicine, Olea ferruginea Royle, olive, olive bark, olive extracts, Olive Leaf, olive oil, olive tree